This is our fifth post of this series on interoperable active RFID and the ISO 18000-7 standard. So far, we have discussed how the standard allows true interoperability in the active RFID technology environment and we have discussed where the value of that standard can be derived in the international shipments market. We have also posited a technical and solution framework that is needed to deliver on the value proposition. We have discussed what has been tried and how those previous efforts fared. Finally, in this post we will discuss some of the current players and a method for evaluating their fit with our evaluation framework.
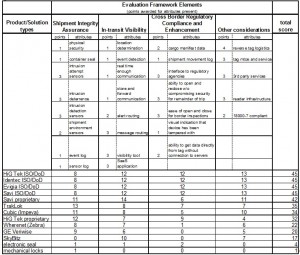
Shown below is a matrix of companies that are competing in some or all aspects of the evaluation framework described in this report. Each vendor has been evaluated and scored on each key business value driver against key attributes that the framework describes as necessary to deliver true business value. The maximum score is 60 points, representing 15 points in each of the four evaluation areas, shipment integrity assurance, in-transit visibility support, cross border compliance enhancement support, and other considerations.
Shipment Integrity Assurance Support
Shipment integrity assurance includes the following attributes:
- Physical security – the ability to lock the container or trailer closed
- Container seal – the ability to identify a seal or tracking number
- Intrusion attempt sensors – the inclusion of sensors that can detect when someone is attempting to break into the container or trailer
- Intrusion deterrence – the ability of the form factor of the tag/lock to delay or inhibit the intruder from actually breaking into the shipment. The intent is for the delay to either discourage or, in some situations, allow an alarm to be sent and security forces to respond and apprehend the intruder
- Intrusion detection sensors – the inclusion of sensors that can detect when the shipment’s integrity has been compromised
- Shipment environment sensors – the inclusion of sensors that monitor key environmental attributes of the inside of the container/trailer
- Event log – the inclusion in the tag or on a server of a log of predefined events
- Sensor log – the inclusion in the tag or on a server of periodic readings of sensor values
In-transit Visibility Support
In-transit visibility support includes the following attributes:
- Location determination –to the level appropriate for the shipment, e.g. latitude/longitude, last known reader location, closest other location marker, etc.
- Event detection – the recognition of an event communicated by the tag that may require routing or alarming
- Real time enough communication – this is the ability to communicate on a pre-defined frequency, either time or event based, appropriate to the shipment’s needs
- Store and forward communication – the ability to store messages at the tag level until such time as the tag can communicate to the reader infrastructure. This capability allows the tag to move in a communication dead zone and then “catch up” when communication is re-established.
- Alert routing – the ability to route alert messages, like alarms, to a specific list of addresses by multiple communications means (e.g. e-mail, text, web service, etc.)
- Message routing – the ability to route routine messages to those stakeholders, service providers, etc. that have interest in the shipment’s movement and events
- Visibility tool – the provision of a means that allows users to access, on demand, the information about the shipment to include alarms, status messages, and current location and condition
- SaaS application – the visibility tool and other associated server applications are provided as a software as a service solution
Cross Border Compliance Enhancement Support
Cross border compliance enhancement support includes the following attributes:
- Cargo manifest data – the information about the cargo associated with the shipment is either on the tag or available on a server via the visibility tool or an interface to a back end system
- Shipment movement log – a log of key shipment movement events
- Interface to regulatory agencies – the interface of key message traffic from the shipment’s events/movement to appropriate regulatory agencies in a certified format acceptable to them. These data further enable the border agencies to clear the shipment through the border more effectively
- Ability to open and re-close the shipment without compromising the security for the remainder of the journey – this is the ability to reset the tag after an authorized breach to indicate that its shipment integrity has not been violated
- Ease of opening and closing for border inspections – an intuitive method with easy instructions to allow border inspections to occur without tag destruction
- Visual means indicating if the shipment integrity has been compromised – an LED or some indicator on the tag
- Ability to interact directly with the tag without connection to servers – typically this is the provision of a handheld terminal and software that can read the contents of the tag. It may also be able to write to the tag
Other Considerations
Other considerations include the following attributes:
- Reverse tag logistics – a means or plan in place to enable the return of the tags to insure that they are reused
- Tag maintenance and service – a means or plan in place to enable maintenance of tags and provide other operational services
- Third party services – a partnership with a 3rd party service provider is in place to enable the previous two points. This may be in addition to or instead of the manufacturer providing those services directly
- Reader infrastructure – an appropriate capability is in place and ready to support the shipment’s movement through the supply chain
- ISO 18000-7 compliant – the solution being offered matches requirements of ISO 18000-7:2008
Competitor Evaluations
As a reminder, this matrix is for only a portion of the competitors that offer active RFID products/solutions. It is not meant to be an exhaustive evaluation by any standard but is meant to show that at least some of the evaluation framework is available today.
Manufacturers in this post include:
Related posts in this series are:
Two Approaches to Standards and Interoperability for Active RFID (aRFID)
Interoperability for active RFID: at last, different vendors work together like passive RFID!
Interoperable RFID – Show me the money!
Interoperable RFID – How will the money be delivered?
Interoperable RFID – Why hasn’t this been done already?